A recent study by the Harvard Undergraduate Association has revealed that generative AI, particularly large language models (LLMs), is significantly influencing the daily routines of students at Harvard University. With nearly 90% of surveyed students incorporating these tools into their academic lives, the findings highlight a transformative shift in how education is approached and experienced.
Overview of the Study
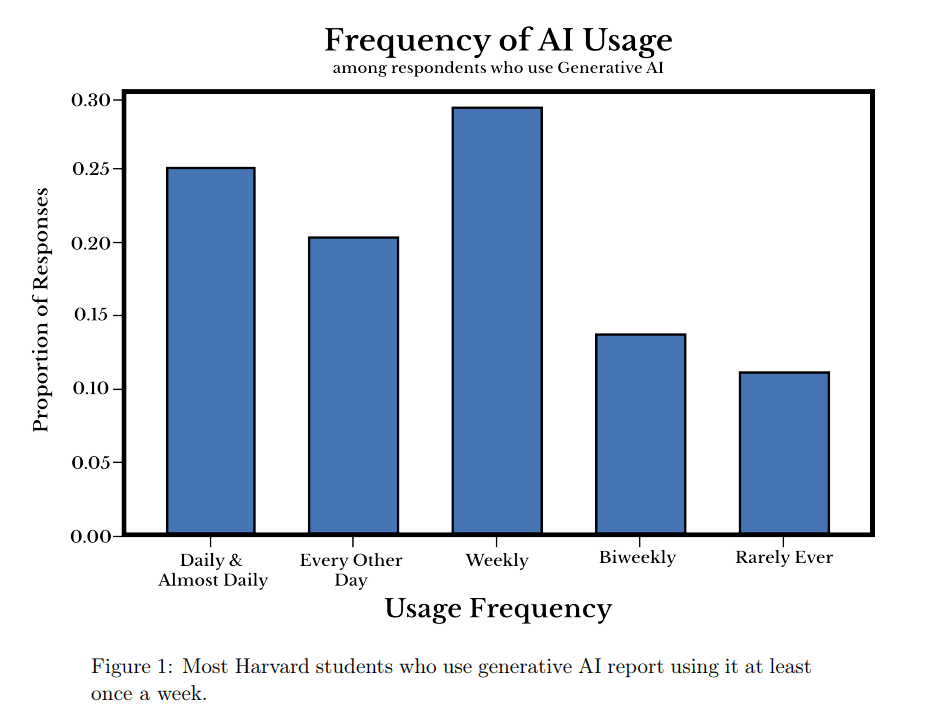
The study surveyed 326 undergraduate students, uncovering that 87.5% of them use generative AI tools regularly. Notably, almost 50% of these users interact with AI at least every other day. This frequency of use indicates a deep integration of AI into students’ academic habits, suggesting that these technologies are not merely supplementary but are becoming essential to their learning processes.
Key Findings
- Substitution for Traditional Learning Methods: Approximately 25% of students indicated that AI tools are beginning to replace traditional academic practices, such as attending office hours or completing assigned readings. This shift raises questions about the future of educational engagement and the role of instructors.
- Replacement of Information Sources: One-third of the respondents reported that they are substituting conventional information sources, like Wikipedia and Google, with AI systems for their research and study needs. This change reflects a growing trust in the capabilities of AI to deliver accurate and relevant information.
- Popularity of Specific AI Tools: OpenAI’s ChatGPT emerged as the most utilized tool, with over 95% of AI-engaged students using it. Other tools, such as Anthropic’s Claude and GitHub Copilot, were used by about 20% of students. This dominance of ChatGPT highlights its effectiveness and popularity among students.
- Concerns About Job Prospects and AI’s Impact: The study also revealed that half of the students are concerned that the rise of AI could negatively affect their job prospects. This apprehension is coupled with a desire for more educational offerings on AI’s future implications, as over half of the respondents expressed a wish for Harvard to provide more classes focused on AI.
- Societal Implications of AI: The survey delved into students’ perspectives on the broader societal impacts of AI. Half of the students expressed worries about AI exacerbating economic inequality, while 40% believe that the existential risks posed by AI should be prioritized similarly to global crises like pandemics and nuclear war.
The Transformative Role of AI in Education
The integration of LLMs into students’ daily routines signifies a pivotal moment in education. As students increasingly rely on AI for academic support, educational institutions must adapt to this new landscape.
Recommendations for Universities
The findings from the Harvard study prompt several recommendations for universities:
- Provide Free AI Access: Ensuring that all students have access to AI tools can help level the playing field, allowing everyone to benefit from these technologies.
- Establish Clear Guidelines for AI Use: Universities should create frameworks that outline how students can ethically and effectively use AI tools in their studies, addressing concerns about academic integrity and the potential for misuse.
- Offer AI-Focused Career Counseling: With students expressing concerns about the impact of AI on job prospects, universities should provide career counseling that incorporates discussions about AI’s role in various industries and how students can prepare for an AI-driven job market.
Pedagogical Innovations
The study’s results suggest that educators should rethink their teaching strategies to incorporate AI effectively. This could involve:
- Integrating AI into Curriculum: Courses could be designed to teach students not only how to use AI tools but also to critically analyze their outputs and understand their limitations.
- Encouraging AI-Enhanced Learning: Educators can leverage AI to create more engaging and personalized learning experiences, using tools to simulate discussions, provide instant feedback, or assist in research.
- Promoting Ethical Discussions: As students navigate the complexities of AI, fostering discussions around the ethical implications of AI use in academia and society will be crucial.
Conclusion
The Harvard Undergraduate Association’s study illustrates that generative AI is becoming a cornerstone of students’ academic experiences. As these technologies continue to evolve, universities must embrace this change, adapting their curricula and support systems to prepare students for a future where AI plays an integral role in education and beyond. The recommendations stemming from this research provide a roadmap for institutions looking to harness the potential of AI while addressing the challenges it presents.This pivotal moment in education calls for collaboration between students, educators, and administrators to ensure that the integration of AI enhances learning outcomes and prepares students for the complexities of an AI-driven world.